Almost all of us have had to deal with manifestations of helminthiasis. These parasites have coexisted with humans for so long that Hippocrates himself mentions them in his writings. According to WHO statistics, currently more than five billion people on Earth are affected by helminthiasis of various types.
The pharmaceutical industry regularly produces modern products designed to neutralize parasites in the human body; even folk remedies for helminthiasis, which complement traditional treatment, have not lost their relevance.
About helminths

There are approximately 250 species of parasites that live in human tissues and organs. All are divided into two classes:
- flatworms (nematodes);
- nematodes (cestodes and trematodes).
Their sizes range from a few millimeters to 10-12 meters, parasites very quickly mature sexually, after which they acquire the ability to lay ten to one hundred thousand eggs per day.
These eggs remain viable for a long time, even if the conditions in which they are found are not the most favorable. Types of organisms affected by parasites, depending on their stage of development:
- the final host in which helminths can develop to the stage of sexual maturity;
- intermediate host, where helminths live until one of the stages of their development.
In the body of the final host, the parasite can complete its entire development cycle many times and live there for several decades. For various types of parasites, humans can be the final or intermediate host, as can crustaceans, fish and carnivores. Based on the type of biological cycle, cases of parasitic infection are classified into:
- biohelminthiasis: the development of helminths occurs in organisms of various species;
- geohelminthiasis: helminth eggs spend part of their development cycle in the soil, without an intermediate host.
How does parasitic infection occur?

The ways in which helminths enter the human body are very different and depend on social characteristics, natural and climatic factors and food preferences. The main methods of helminth infection:
- Through dirty hands, contaminated water, poorly processed food.
- When inhaling dust particles containing worm eggs.
- Through the skin.
- After a mosquito bite as an intermediate host (Wuchereria bancrofti).
- When eating contaminated seafood, meat, fish (flukes).
The eating habits of some northern peoples suggest the use of lightly salted and raw fish. The prevalence of trichinosis and echinococcosis is high in this population.
Which organs are affected by helminthiasis?
Helminth damage can be localized to many organs and tissues. The localization of helminth depends on the stage of its development, so the same type of worm at different stages of its existence can parasitize in different parts of the intestine. Organs affected by helminthiasis:
- Large intestine: roundworms, pinworms.
- Duodenum: Strongyloides stercoralis.
- Lymphatic vessels.
- Lungs – Paragonimidae.
- Subcutaneous tissue - Larva migrans.
- Helminths parasitize hollow organs and tissues of the human body.
Depending on the location of the parasites, helminth infections are divided into types:
- tissue (echinococcosis, cysticercosis);
- luminal (taeniasis, enterobiasis, ascariasis).
Some helminths in the larval stage transform the tissues of the human body, forming capsules or granules around themselves (Trichinella, Toxocara). There is a type of helminths that migrate to the larval stage both under the skin of a person and in the tissues of his organs (larval helminths).
Their temporary residence in the human body takes both visceral and cutaneous forms; for them man is an intermediate host.
Clinical manifestations of helminthiasis
Like many other infections, helminthiasis goes through two stages of development: acute and chronic. Their duration:
- acute stage – from 2-3 weeks to several months;
- chronic stage – from 2-3 months to several years.
Despite the variety of types of helminths and their localization, the symptoms of the acute phase have common manifestations: these are symptoms of allergies and toxic effects on the human body:
- slight increase in temperature
- muscular pain,
- skin rashes,
- swelling of the limbs,
- swollen lymph nodes,
- dyspepsia,
- enlargement of the spleen and liver,
- damage to the central nervous system.
A laboratory blood test indicates a change in its formula: eosinophilia and a significant increase in the number of leukocytes are diagnosed. The transition of helminthiasis to the chronic stage is marked by symptoms depending on the organ affected by the parasites, the stage of development of the worms, their number and variety. In the chronic stage of helminthiasis, the following symptoms are diagnosed:
- dyspepsia and intestinal pain,
- intestinal blockage,
- hemorrhagic colitis,
- anemia,
- avitaminosis,
- sudden weight loss,
- obstructive jaundice, hepatitis (with liver damage),
- loss of some functions of the central nervous system (when the parasites are localized in the brain),
- inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (with migration of pinworms into the vagina),
- stomach and intestinal ulcers (with chronic strongyloidosis),
- damage to muscle tissue, formation of granulomas in the capillaries of the brain (with severe trichinosis),
- damage to the lymphatic system (due to roundworm infection).
In helminthiasis caused by echinococci not only liver cysts form, but also bone tissue can be damaged by the parasites. This makes bones brittle and creates an additional risk of bone fractures. Damage to the human body by the larvae of Dirofilaria repens occurs in the form of the formation of a subcutaneous node containing parasites. This node is able to move through the thickness of the skin and mucous membranes.
Analyzing the symptoms of helminthiasis, one can be convinced that there is no stable clinical picture of this disease or clear specific signs.
Diagnosis of parasite infestation
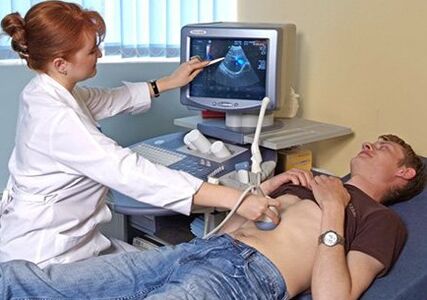
If an accurate diagnosis is not made in time, you may miss the time when treatment could be most effective.
The transition of helminthiasis from the acute phase to the chronic form often masks the true cause of the disease.
Parasite infection can be confused with symptoms of completely different diseases. It is extremely important not to self-medicate, but to seek medical help from an infectious disease specialist or parasitologist. Its arsenal includes numerous modern methods for diagnosing parasitic infestations:
- laboratory examination of feces, bile, sputum, blood, urine, scrapings of rectal and anal mucus, duodenal contents for the detection of parasites, their eggs and larvae;
- Ultrasound, radiography;
- endoscopy, endobiopsy.
The most effective method is considered to be a serological test, a method of analyzing blood serum for the presence of antigens for infection with certain types of helminths.
This test can reveal the presence of parasites even in the early stages of the infection.
Treatment of parasitic infections with traditional methods

Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor prescribes anthelmintic therapy and the timing of the control study after treatment.
All specialist recommendations should be followed carefully to avoid complications.
There is no need to remember to observe preventive hygiene measures that will prevent parasites from infecting family members and causing secondary infections.
Supporters of the use of traditional recipes must remember that the use of these remedies is an auxiliary method that does not replace drug treatment.
Like medicines, traditional medicine also has contraindications and side effects. That's why it's worth discussing this method with your doctor before using them. Home Remedies:
- Consume peeled pumpkin seeds for 2 weeks, keeping the thin green skin of the seed.
- A decoction of the peel removed from a pomegranate in 3/4 tablespoons. boiling waterThe remedy is drunk on an empty stomach; this must be done an hour and a half before, dividing the decoction into three doses. After a few hours, be sure to stimulate the stool with any laxative.
- Enemas with freshly squeezed carrot juice (40 ml) should be done every day for 7 days.
- Regular consumption of garlic and preparations containing it.
- Introduce a whole clove of garlic into the rectum (against enterobiasis).
- Take freshly prepared garlic juice (10-15 ml) along with warm milk (1 glass), drink the mixture on an empty stomach, repeat the intake 1-2 times during the day.
- Infusion of 50 g of a mixture of garlic and grated horseradish root in half a liter of vodka. The mixture is infused for 1. 5 weeks, filtered. Mandatory dose – 1 tablespoon. L. Before each meal, the infusion must be washed. Effective against giardiasis.
- An enema with garlic gruel, taken shortly before bedtime, is effective against pinworms and tapeworms. Enema solution: Mix 1 teaspoon in a glass of water. finely chopped garlic. Carry out regularly throughout the week.
- Decoction of 2 cloves of garlic, 2 tbsp. milk, 1 tbsp. L. dried tansy flowers are administered as an enema. The enema mixture should be boiled for about 10 minutes. Carry out 7 times, the effect of treatment can be consolidated by repeating the course after a ten-day break.
Herbs and taxes:
- 1 Teaspoon. dried wormwood, pour 400 ml (2 tablespoons) of boiling water, strain and cool, take an infusion of 1-2 tablespoons. L. three times a day before each meal. Effective against ascariasis and enterobiasis.
- Infuse tansy (1 tablespoon of dried flowers) and 0. 5 liters of boiling water for 3 hours and administer as an enema into the rectum before bedtime. The product is contraindicated for pregnant women and children.
- Infusion for half an hour from 4 tablespoons. L. unripe nuts and a glass of boiling salted water, filtered and taken simultaneously with a laxative. Effective against tapeworm, ascariasis, enterobiasis.
- 1 tablespoon. L. Pour 200 ml of boiling water over the tansy flowers and filter the infusion after an hour. The admission frequency is standard - Art. l. 20 minutes before meals. Then you need to be treated for 2-3 days, finish taking the infusion with a laxative.
- A decoction of 1 kg of sorrel and 1 liter of boiling water is boiled for 2 hours (it is better to do this in a water bath), filtered and a couple of spoons of sugar are added. The volume of the final product is 1 glass of decoction, it should be drunk 1-2 sips a day before meals.
Helminthiases are complex infections with a multicomponent clinical picture. They can cause serious complications and cause irreversible damage to human health.
It is unacceptable to self-medicate if infected with parasites. Traditional recipes should be used with extreme caution, only as an adjunct to accompany drug therapy.